spike and dome membranous nephropathy|A First Step toward a New Approach to Treating Membranous : Clark MGN is caused by immune complex formation in the glomerulus. The immune complexes are formed by binding of antibodies to antigens in the glomerular basement membrane. The antigens may be part of the basement membrane, or deposited from elsewhere by the systemic circulation. . Tingnan ang higit pa ¡Registrarse en 888sport! Descargar 888sport en Android. 888sport recomienda descargarte una aplicación Android apuestas deportivas desde Google Play, en este caso, su app de apuestas, 888 Sport. Al descargar app 888sport android disfrutarás en tu dispositivo móvil o tablet de una de las aplicaciones más utilizas en la .
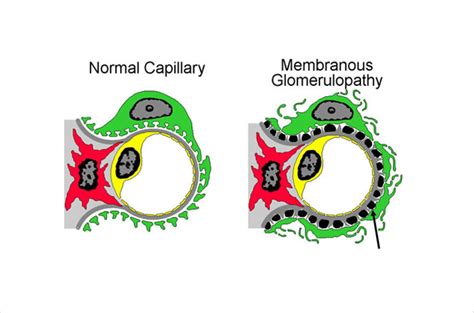
spike and dome membranous nephropathy,MGN is caused by immune complex formation in the glomerulus. The immune complexes are formed by binding of antibodies to antigens in the glomerular basement membrane. The antigens may be part of the basement membrane, or deposited from elsewhere by the systemic circulation. . Tingnan ang higit paMembranous glomerulonephritis (MGN) is a slowly progressive disease of the kidney affecting mostly people between ages of 30 and 50 years, usually white people (i.e., those of European, Middle Eastern, or North African Tingnan ang higit paThe defining point of MGN is the presence of subepithelial immunoglobulin-containing deposits along the glomerular basement membrane Tingnan ang higit paAbout a third of untreated patients have spontaneous remission, another third progress to require dialysis and the last third continue to have proteinuria, without. Tingnan ang higit paMost people will present as nephrotic syndrome, with the triad of albuminuria, edema and low serum albumin (with or without . Tingnan ang higit pa
Traditional definitions split membranous nephropathy into 'primary/idiopathic' or 'secondary'. It is likely that instead the field will . Tingnan ang higit pa
Treatment of secondary membranous nephropathy is guided by the treatment of the original disease. For treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy, the treatment . Tingnan ang higit pa
The closely related terms membranous nephropathy (MN) and membranous glomerulopathy both refer to a similar constellation but without the assumption of. Tingnan ang higit pa
Membranous nephropathy (MN) is a common cause of proteinuria and nephrotic syndrome all over the world. It can be subdivided into primary and secondary . Membranous nephropathy (MN), also known as membranous glomerulopathy, is one of the many glomerular diseases causing nephrotic syndrome. It is characterized by massive . Primary membranous nephropathy (PMN) is one of the common causes of adult-onset nephrotic syndrome and is characterized by autoantibodies against .Membranous nephropathy (MN) is a common cause of adult nephrotic syndrome and is seen less commonly in children. The field has advanced significantly and rapidly in the . Membranous nephropathy is a glomerular disease that is the most frequent cause of nephrotic syndrome in adults. This Primer reviews the . Membranous nephropathy (MN) is among the most common causes of the nephrotic syndrome in adults without diabetes, accounting for up to one-third of biopsy .

The morphological hallmark of membranous nephropathy (MN) is the presence of immune deposits that contain immunoglobulins and antigens in the .
Membranous nephropathy, the leading cause of nephrotic syndrome in adults (approximate incidence among white adults without diabetes, 8 to 10 cases per .
Membranous nephropathy is deposition of immune complexes on the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) with GBM thickening. Cause is usually unknown, although .
Membranous nephropathy (MN) is a common cause of proteinuria and nephrotic syndrome all over the world. It can be subdivided into primary and secondary forms. . (“spikes and domes”). Mesangial electron deposits are absent or scanty in primary MN (Table 1). Open in a separate window. Figure 1. Primary membranous . Membranous nephropathy (MN) is a common cause of proteinuria and nephrotic syndrome all over the world. It can be subdivided into primary and secondary forms. Primary form is an autoimmune .Membranous Nephropathy (MN) affects men twice as often as women and is more common in adults between the ages of 40 and 70. It develops slowly, over a number of years and people may not realise they have the disorder. Some are identified simply because they are found to have a lot of protein in their urine after a routine test (see .Membranous nephropathy is deposition of immune complexes on the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) with GBM thickening. Cause is usually unknown, although secondary causes include medications, infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancer. Manifestations include insidious onset of edema and heavy proteinuria with benign .Membranous nephropathy (MN) is an immune complex disease caused by subepithelial deposits. Primary MN is a common cause of nephrotic syn-drome. About a third of patients reach remission, a third are stable, and a third have progressive loss of kidney function and persistent proteinuria. The phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R), expressed on .spike and dome membranous nephropathy Clinical definition. a type of kidney disease that results in proteinuria, peripheral edema, hyperlipidemia, and hypoalbuminemia. Associated conditions. chronic kidney disease. HBV. membranous nephropathy. Epidemiology. Incidence. annually there are 3 cases per 100,000 adults.Abstract. Membranous nephropathy (MN) is the most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in non-diabetic Caucasian adults over 40 years of age. It has an estimated incidence of 8-10 cases per 1 million. Fifty per cent of patients diagnosed with primary MN continue to have nephrotic syndrome and 30% of patients may progress to end-stage .Membranous nephropathy (MN) is a condition that causes your immune system to attack glomeruli, the tiny filters in your kidney. Your kidneys have thousands of glomeruli. These filters clean waste products from your blood. If you have membranous nephropathy, your glomeruli become inflamed. MN can cause your kidneys to stop filtering waste as .Membranous Glomerulonephritis . Membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN) is a disease characterized by subepithelial immune deposits, thickening, usually diffuse, of the glomerular capillary walls, and, in many cases, formation of perpendicular projections of material similar to the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) in the external part of this .

Membranous nephropathy (MN) is the most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in non-diabetic Caucasian adults over 40 years of age. It has an estimated incidence of 8–10 cases per 1 million. Fifty per cent of patients diagnosed with primary MN continue to have nephrotic syndrome and 30% of patients may progress to end-stage .
Membranous nephropathy is the most common cause of primary nephrotic syndrome in adults, most often presenting in the fifth and sixth decades. . a “spike and dome” pattern results from projections of excess GBM between the subepithelial immune complex deposits (eFigure 22–16). Immunofluorescence shows IgG and C3 staining along capillary .
Membranous nephropathy is caused by deposition of antibody- antigen immune complexes beneath epithelial podocyte and on the outer surface or/ and inside the glomerular basement membrane .A First Step toward a New Approach to Treating Membranous A silver stain of the glomerulus highlights the proteinaceous basement membranes in black. There are characteristic "spikes" of basement membrane between the immune deposits of membranous .
Membranous nephropathy is deposition of immune complexes on the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) with GBM thickening. Cause is usually unknown, although secondary causes include medications, infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancer. Manifestations include insidious onset of edema and heavy proteinuria with benign .spike and dome membranous nephropathy A First Step toward a New Approach to Treating Membranous Abstract. Membranous nephropathy (MN) is one of the most common causes of non-diabetic nephrotic syndrome in adults. About 80% of cases are renal limited (primary MN) and 20% are associated with other systemic diseases or exposures (secondary MN). Autoimmune reaction is the main pathogenic factor of MN, and the . Clinical definition. a type of kidney disease that results in proteinuria, peripheral edema, hyperlipidemia, and hypoalbuminemia. Epidemiology. incidence. annually there are 3 cases per 100,000 adults. Etiology. primary glomerular disease. focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. membranous nephropathy.Membranous nephropathy (bubbling appearance and spike formation) without immunoglobulin deposition in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus Clin Exp Nephrol. 2008 Dec;12(6):475-8. doi: 10.1007/s10157-008-0096-8. . Glomerulonephritis, Membranous / pathology* Membranous nephropathy (MN) is a major cause of nephrotic syndrome(NS) in adults. . and 1 small fibrocellularcrescents.GBM thickening and “spike and dome” appearance were observed. Renal tubules presented with epithelial cells granular degeneration with few protein casts. The interstitium was infiltered by .
spike and dome membranous nephropathy|A First Step toward a New Approach to Treating Membranous
PH0 · Secondary Membranous Nephropathy. A Narrative Review
PH1 · Membranous nephropathy: new pathogenic mechanisms and
PH2 · Membranous nephropathy: Clinical manifestations and diagnosis
PH3 · Membranous nephropathy: Clearer pathology and mechanisms
PH4 · Membranous nephropathy
PH5 · Membranous glomerulonephritis
PH6 · Membranous Nephropathy: Core Curriculum 2021
PH7 · Membranous Nephropathy
PH8 · A First Step toward a New Approach to Treating Membranous